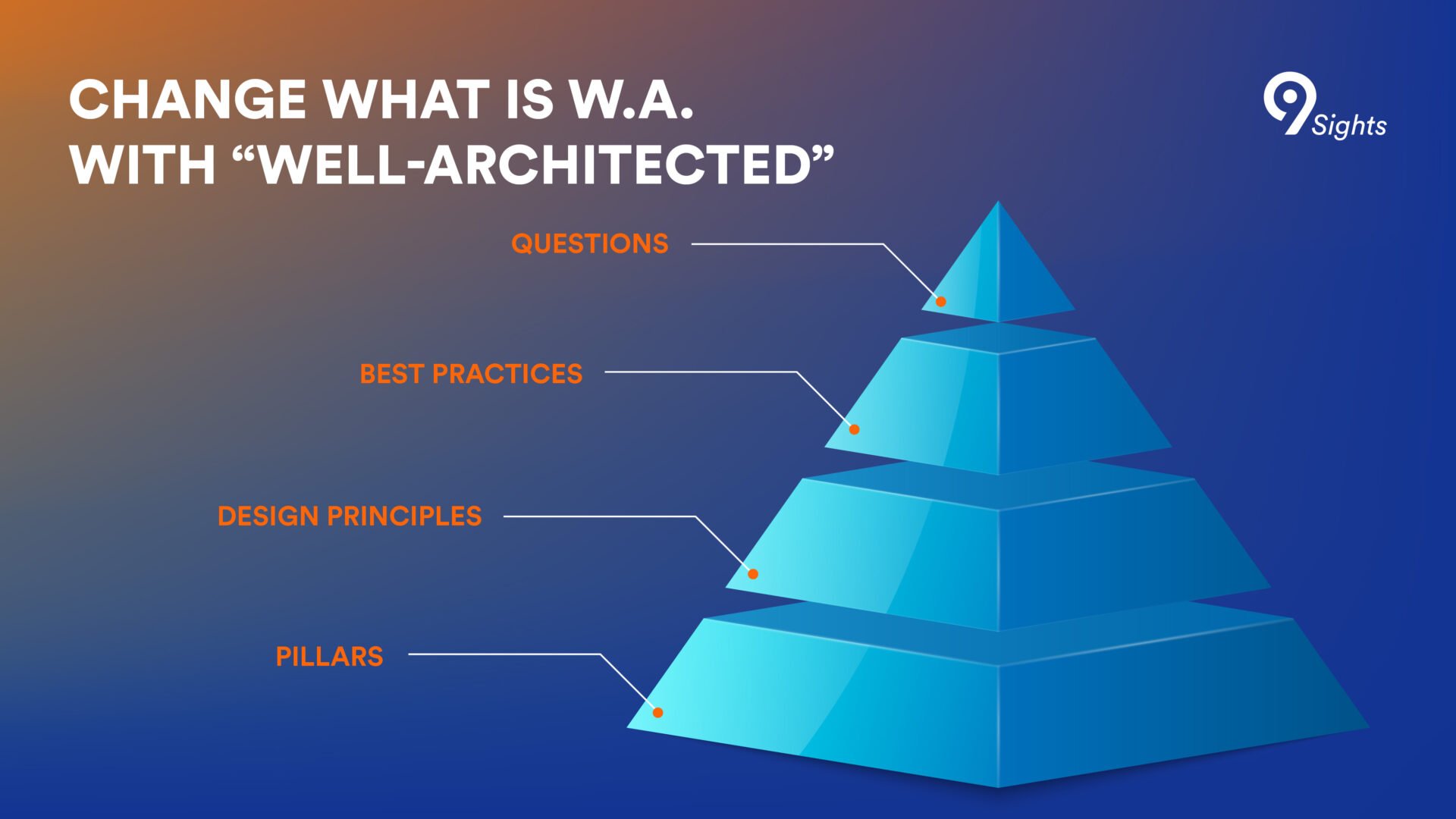
AWS Well-Architected Framework
Operational Excellence: Focuses on operations, monitoring, and continual improvement.
Security: Emphasizes data protection, privilege management, and continuous risk assessment.
Reliability: Ensures workloads can recover from failures and meet customers' demands.
Performance Efficiency: Involves using IT resources efficiently.
Cost Optimization: Helps manage and reduce costs.
Detailed View with Principles and best practices:
Operational Excellence
Principles: Design systems to monitor and improve operational processes.
Best Practices:
Implementing automation for tasks like deployment and recovery.
Regularly reviewing and refining operational procedures.
Establishing mechanisms for monitoring, logging, and alerting.
Example: A global e-commerce company
Scenario: The company has a complex architecture involving multiple microservices, which must be continuously deployed and monitored to ensure smooth operation.
Implementation:
Automation: The company uses AWS CodePipeline for CI/CD to automate the deployment process, ensuring that updates are consistently and reliably applied without manual intervention.
Monitoring: AWS CloudWatch is set up to monitor system performance, log application metrics, and trigger alarms when thresholds are breached.
Improvement: Regular review meetings are held to analyze incidents and refine operational processes based on the insights gained.
Security
Principles: Protect information, systems, and assets while delivering business value.
Best Practices:
Implementing strong identity and access management.
Using encryption to protect data at rest and in transit.
Enabling continuous security auditing and monitoring.
Applying security best practices like least privilege access.
Example: A financial services firm
Scenario: The firm needs to protect sensitive customer data and comply with stringent regulatory requirements.
Implementation:
Identity and Access Management: AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) is used to enforce the principle of least privilege, ensuring that employees only have access to the resources necessary for their job roles.
Encryption: AWS Key Management Service (KMS) is used to encrypt data at rest, while AWS Certificate Manager handles encryption for data in transit.
Continuous Monitoring: AWS Config and AWS CloudTrail are used for continuous compliance and auditing, providing visibility into resource configurations and user activities.
Reliability
Principles: Ensure workloads perform their intended functions correctly and consistently.
Best Practices:
Designing for failure with robust recovery plans.
Automating recovery processes to improve reliability.
Scaling horizontally to distribute the load and reduce single points of failure.
Regularly testing recovery procedures.
Example: An online video streaming service
Scenario: The service needs to ensure high availability and resilience to handle large volumes of traffic during peak times, such as major live events.
Implementation:
Failover Strategy: AWS Route 53 is used to route traffic across multiple AWS regions, providing automatic failover in case of regional outages.
Auto Scaling: AWS Auto Scaling is employed to automatically adjust the number of EC2 instances based on traffic demand, ensuring that the service can handle load spikes without manual intervention.
Data Backup: Regular snapshots of databases are taken using Amazon RDS, and these snapshots are stored in different regions to provide redundancy.
Performance Efficiency
Principles: Use resources efficiently to meet system requirements and maintain efficiency as demand changes.
Best Practices:
Selecting the right resource types and sizes based on workload needs.
Monitoring performance and making data-driven decisions.
Utilizing serverless architectures to reduce overhead.
Employing caching and CDN services to improve performance.
Example: A mobile gaming company
Scenario: The company needs to ensure that its game servers are highly responsive and can scale efficiently to accommodate fluctuating user loads.
Implementation:
Resource Selection: The company uses Amazon EC2 Spot Instances to reduce costs while maintaining the ability to scale rapidly. They also utilize Amazon DynamoDB for its low-latency, scalable database services.
Caching: Amazon CloudFront is used as a content delivery network (CDN) to cache static assets closer to users, reducing latency and improving load times.
Performance Monitoring: AWS X-Ray is used to analyze and debug application performance, helping identify bottlenecks and optimize resource usage.
Cost Optimization
Principles: Avoid unnecessary costs and invest in a cost-effective architecture.
Best Practices:
Adopting a consumption model to pay only for what you use.
Analyzing and attributing expenditure to maximize cost efficiency.
Using managed services to reduce operational overhead.
Scaling to match demand and avoid over-provisioning.
Example: A startup offering SaaS solutions
- Scenario: The startup needs to manage its operational costs while scaling its services as its user base grows.
Implementation:
Right Sizing: The startup conducts regular reviews of its EC2 instance usage and right-sizes its instances to match the current demand, avoiding over-provisioning.
Reserved Instances: For predictable workloads, the startup purchases Amazon EC2 Reserved Instances to lower costs compared to on-demand pricing.
Cost Monitoring: AWS Cost Explorer and AWS Budgets are used to track spending and set up alerts for unexpected cost increases, allowing the company to stay within budget.
These real-time examples illustrate how different organizations apply the AWS Well-Architected Framework to address specific challenges and optimize their cloud environments across the five pillars.
